RAPEEPUN KALAYAVINAI,M.D.
DOCTOR PROFILE
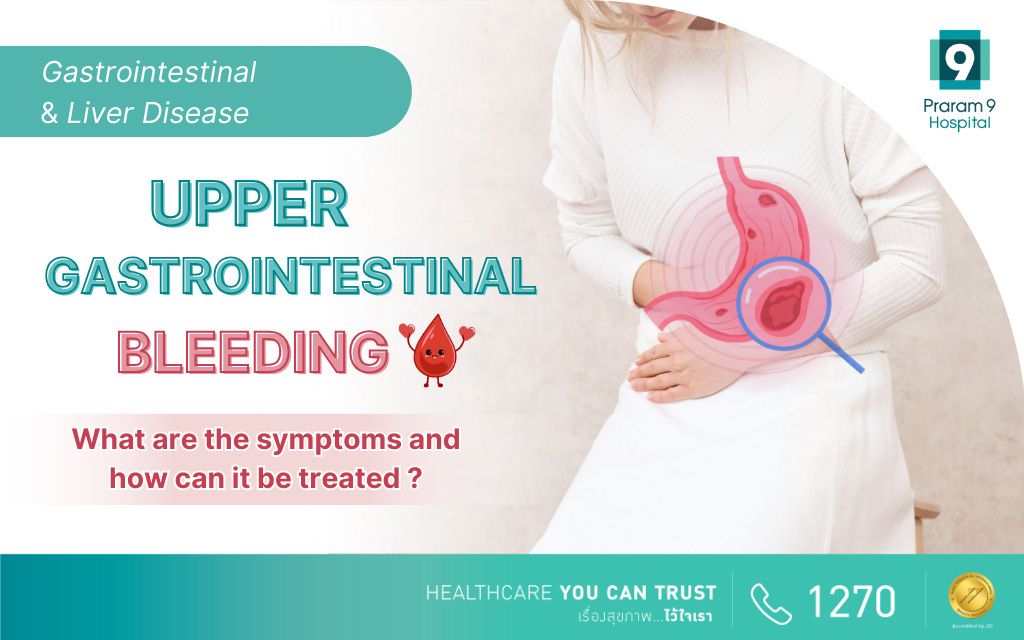
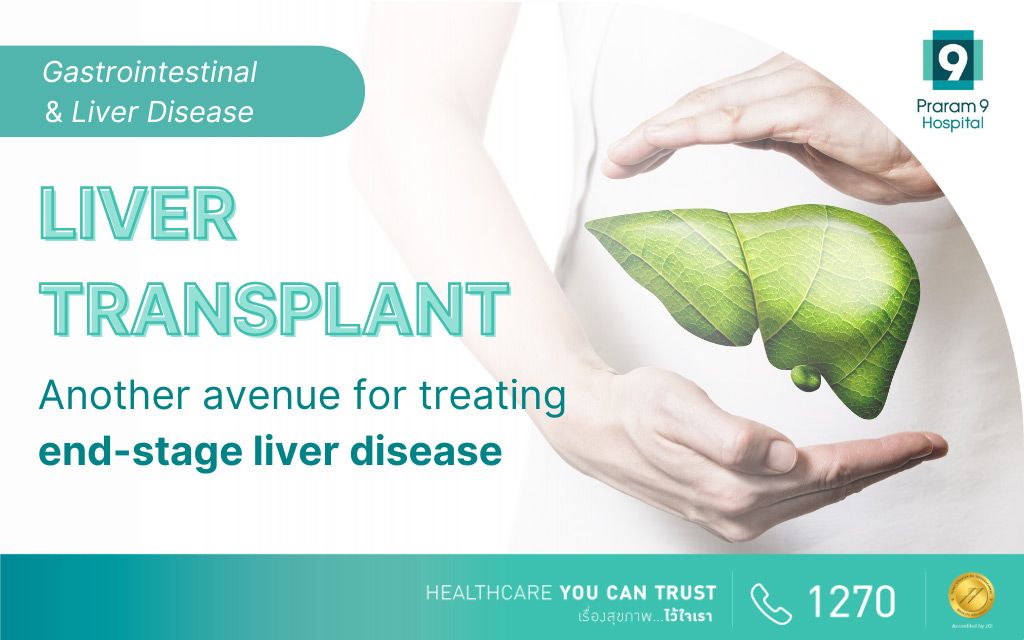
Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease Center
Doctor's Availability Schedule
*Select a day to see the doctor's schedule
Personal Profile
Education
- Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital Mahidol University
- Medicine Bhumibhol Adulyadej Hospital
- Gastroenterology Chulalongkorn University
Academic Position
Association/Club Positions
Research
Learning
Interest
Expert
- Specialist in Gastroenterology
Personal Profile
Education
- Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital Mahidol University
- Medicine Bhumibhol Adulyadej Hospital
- Gastroenterology Chulalongkorn University
Research
Learning
Interest
Expert
- Specialist in Gastroenterology
Academic Position
Association/Club Positions
Doctor's Availability Schedule
*Select a day to see the doctor's schedule